Which Security Level?
We gratefully acknowledge the support of HSM in the presentation of the information below. The full range of high-quality, German-made HSM shredders can be seen by clicking here.
Strip Cut Shredders
Strip-cut shredders (also known as ribbon-cut) are known as "strip-cut shredders" because of the thin strips they create as they shred paper. These strips can vary in size from 12mm wide to 2mm wide. Strip-cut shredders require less cutting than cross-cut shredders. Because less cutting is required, strip-cut shredders are able to shred more sheets at a time than cross-cut shredders (of the same class).
Cross Cut Shredders
Cross-cut shredders (also known as confetti-cut) create small particles of paper. These particles of paper vary in size from 10mm x 80mm to 1mm x 5mm. Cross-cut shredders are not able to shred documents as quickly as strip-cut shredders (of the same class) due to the extra cutting involved. Although they can't shred documents as quickly, cross-cut shredders are able to provide more security to shredded documents than a strip-cut shredder. The shredded waste has less volume, thus requiring less emptying and trips to the bin. Micro-cut; high-security micro-cut; and crypto cut are all also forms of cross-cut with a very small particle size for greater security.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
After the introduction of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018, which standardised the rules for processing personal data throughout Europe, the issue of data protection has become increasingly important.
Data is collected and processed in almost every organisation. It is essential to protect this sensitive data and to prevent unauthorised persons from gaining access to it at any time. However, not only the protection of actively used data must be guaranteed, but also the destruction and disposal of this sensitive data when it is no longer being used in accordance with the law and data protection regulations.
If breaches occurs in the handling of personal data or due to its improper disposal, companies can incur severe fines.
That the subject of data protection also includes the correct destruction of these data is regulated by law. Documents that are in non-digital form must also be destroyed in accordance with these legal requirements, such as files and documents on data media.
Despite these legal requirements, the use of document shredders with the wrong security level or neglecting to use a document shredder at all are still amongst the most common data protection gaps. Documents with personal data do not belong in a waste bin, but in a GDPR-compliant document shredder.
If files and documents contain personal data, their destruction in accordance with data protection laws must be carried out without fail. The use of a GDPR-compliant document shredder is recommended for this purpose. Just shredding such documents at all goes some way towards GDPR compliance, but in general The Shredder Warehouse recommends a GDPR-compliant shredder with a security level of at least P-4. The amount of data to be destroyed, the sensitivity of the data and other criteria should also be considered when purchasing a suitable shredder with a suitable security level. Please feel free to call us on 01225 690700 to discuss your requirements if you are unsure which security level is most appropriate for your application.
For data with higher sensitivity, we recommend the purchase of a shredder with a higher security level. These levels are determined by ISO/IEC 21964 (DIN 66399). Please scroll down to view full details of the International Standard for Security Levels.
What is NPSA (formerly CPNI)?
NPSA (formerly CPNI) stands for National Protective Security Authority and is the government authority for protective security advice to the UK national infrastructure. Its role is to protect national security by helping to reduce the vulnerability of the national infrastructure to terrorism and other threats. It is accountable to the Director General of MI5. NPSA has evaluated and given approval to certain makes and models of shredder as meeting the NPSA Standard – Secure Destruction of Sensitive Items. The NPSA shredders in this section of our website have been evaluated and approved as meeting the NPSA standard and are therefore authorised to carry the NPSA Trademark. If you require a shredder that meets NPSA approval, you can search for “NPSA” on our website; select “NPSA” from the "Shop by category" dropdown menu on our home page; or click here.
International Standard for Security Levels
The old international standard DIN 32757 for shredder security levels was superceded by DIN 66399 some years ago.
The storage media containing our confidential data and information are varied. Along with paper, the classic data medium, digital data media now also plays a major role. The DIN 66399 standard takes this diversity into account, and defines what security means for all our modern media.
DIN 66399 supercedes DIN 32757 and describes the requirements for machines and processes for shredding data media. The standard was developed by the Standards Committee for Information Technology and Applications (NIA).
1. The 3 protection classes of the DIN 66399
The protection requirement of your data is classified into three different classes. The type of data is checked to determine
the protection requirement in the company. This identifies which need for protection is required, and therefore the
protection class.
| Protection 1: Normal security requirement for internal data. | Unauthorised publication or dissemination would have a limited negative impact on the company. Protection of personal data must be ensured. There would otherwise be a risk to the position and financial situation of the affected persons. |
| Protection 2: High security requirement for confidential data. | Unauthorised dissemination would have a considerable affect on the company and could infringe legal obligations or laws. The protection of personal data must fulfil strict requirements. There would otherwise be a considerable risk to the social standing and financial situation of the affected persons. |
| Protection 3: Very high protection requirements for particularly confidential and secret data. | Unauthorised dissemination would have serious terminal consequences for the company and infringe trade confidentiality obligations, contracts or laws. It is essential that the confidentiality of personal data is maintained. Otherwise there is a risk to the health and safety or personal freedom of the affected persons. |
2. The 6 data media of the DIN 66399
The standard divides all the different data media into 6 categories. Each category contains an explanation of the data formats.

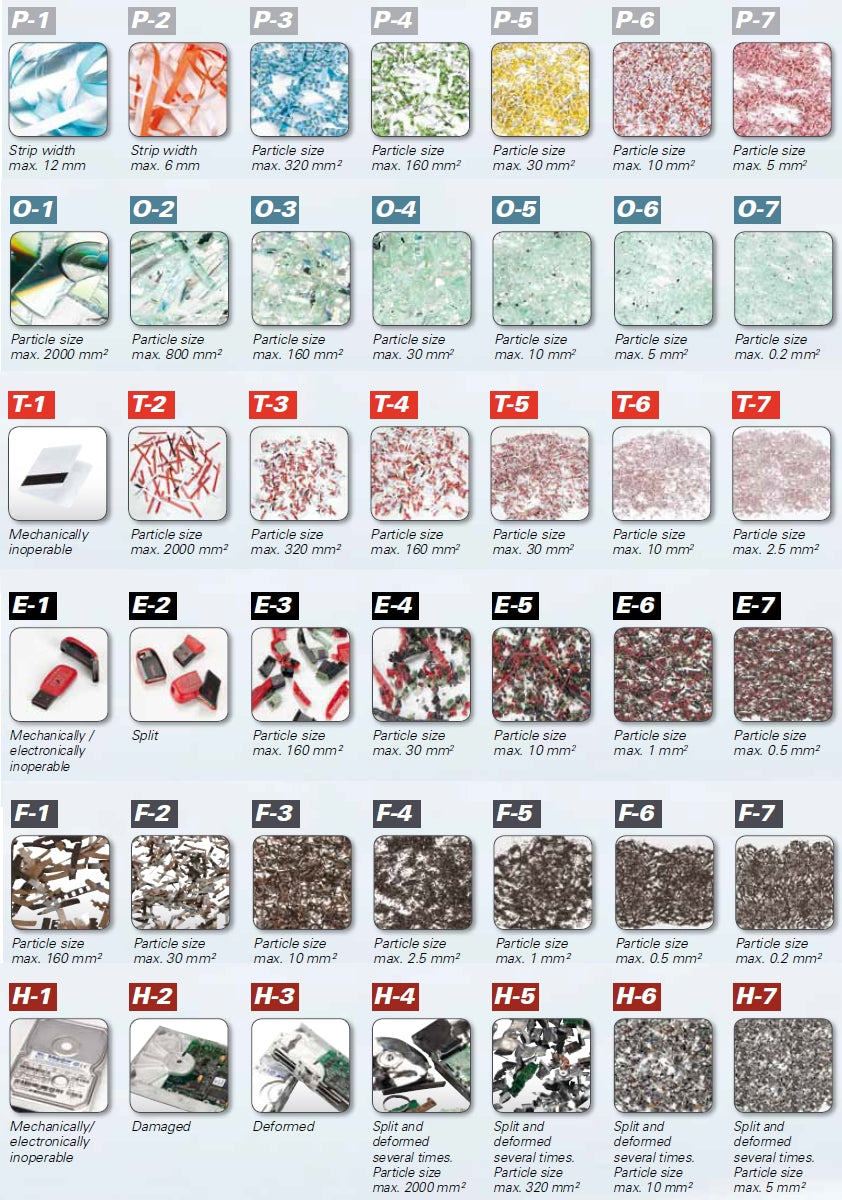
3. The 7 security levels of the DIN 66399
The DIN 66399 standard divides each data media category into 7 security levels. The higher the security level, the smaller the particles.
| Security levels | |
| Protection class 1 | 1, 2 & 3 |
| Protection class 2 | 3, 4 & 5 |
| Protection class 3 | 5, 6 & 7 |
| Security level 1: | General documents to be rendered illegible or invalidated. |
| Security level 2: | Internal documents to be rendered illegible or invalidated. |
| Security level 3: | Data media with sensitive and confidential data as well as personal data subject to high |
| protection requirements. |
| Security level 4: | Data media with highly sensitive and confidential data as well as personal data subject to |
| high protection requirements. |
| Security level 5: | Data media with confidential information of fundamental importance for a person, company |
| or institution. |
| Data media with confidential documents in the case of extraordinary security precautions. |
| For strictly confidential data with the highest security precautions. |
4. All data carrier categories and security levels
The security level which the document shredder produces depends on its cutting units.
The following picture shows the 6 data carrier categories and 7 security levels.